Exploring the Complexities of Peace Agreement Design
More complex peace agreements with a greater number of provisions correspond with a greater probability of failed implementation and of armed conflict recurrence.

In The United States, Right-Wing Terrorism Is On The Rise
The number of terror attacks in the U.S. known to be motivated by right-wing ideologies has grown by over 35% in the last 7 years. Peace Science has found that symbolic targets, gender relations, and threats to identity and privilege are more important to motivating right-wing terrorism than objections to policy or material or economic factors.

Abandoning the INF Treaty Makes the World Less Secure
The United States has announced their withdrawal from the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces (INF) treaty. Abandoning the treaty would make the world, especially Europe, less secure and mark another Cold-War-style arms race.

UNSCR 1325 Has Fallen Short of its “Transformative Potential”
Eighteen years later, the “gender perspective” required by Resolution 1325 has fallen short of its transformative potential. Peace practitioners must turn their gender lenses inward to examine their own cultures and practices as potentially part of the dual problems of gender inequality and insecurity.
Pitfalls of Top-Down Peacebuilding
The top-down approach to peacebuilding has largely failed at creating sustainable peace in places such as Afghanistan, Congo, Iraq, and South Sudan. Yet, a small Congolese island in Lake Kivu has kept the peace despite holding known prerequisites for violent conflict. Their success is largely due to an emphasis on the local’s role in conflict transformation.
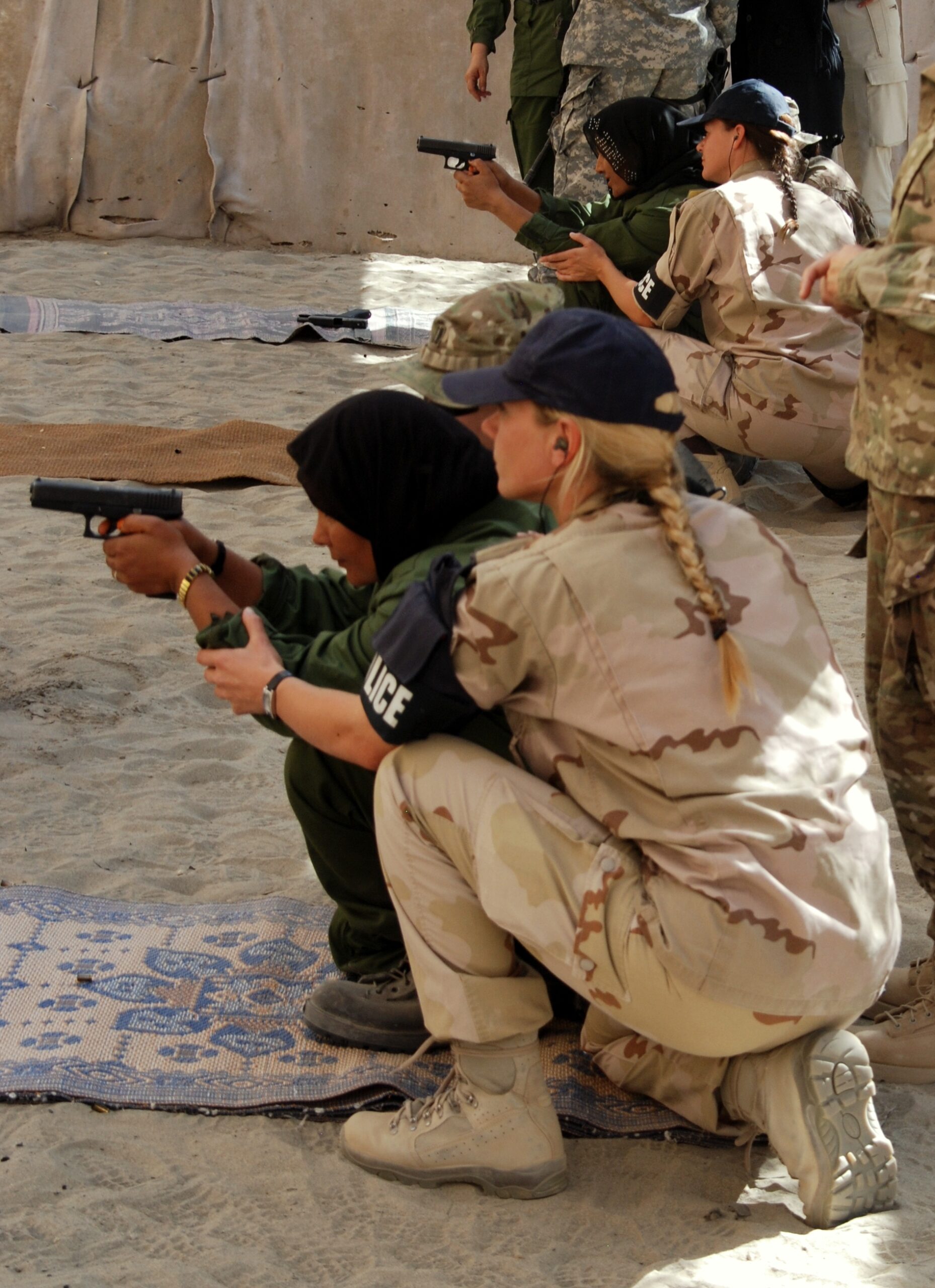

Female Inclusion in Afghan Security Forces: “Get on board or get out — it’s happening”
Militarism, warfare, and the military itself all depend on gender hierarchies—the privileging of masculinity and its associated traits over femininity and its associated traits—to function. Women in Afghanistan are especially aware of this of sexism and inequality as they seek to join their country’s military and police force.

EPA Considers Rolling Back Radiation Exposure Protections
The EPA is considering rolling back regulations on radiation exposure. This is a horrible idea, just ask the victims of nuclear weapons testing in the Pacific.

Special Issue: Gender & Conflict
If there is a silver lining to the current political situation in the U.S., it is the way that polarization can bring latent conflict—in the form of extreme inequality and oppression—to the surface to be addressed. In 2018, one would hope that we would not still be living in a sexist, gender-unequal society (or a racist society, for that matter). But, whereas a few years ago, well-meaning people of all genders might have been able to overlook the ways in which gender (and racial) inequalities still permeate our daily existence, today it is difficult to do so any longer. The courageous revelations of hundreds of women across professions have exposed the insidious ways in which sexual assault and harassment still very much structure power dynamics in the workplace and beyond. Comparisons between world leaders about the size of their nuclear “buttons” have made evident how the desire to look more masculine assists in escalating international conflict. In other words, it is no longer possible to ignore the “work” gender does in politics—from the bedroom to the boardroom to the battlefield.

Weaponized Sexuality: Sexist and Homophobic Propaganda During the Russo-Ukrainian War
When supplemented with the promise of reseating Russia as a great world power, propaganda infused with state-sanctioned homophobia and praise for the traditional “macho” masculine ideology has successfully maintained public support for Russian military action against Ukraine.

Global/Local Interactions and Women’s Participation in Conflict and Peacebuilding in Bougainville
In the case of Bougainville, women leaders emphasized their peacebuilding role in the conflict, drawing on both local customs and norms—like their “maternal responsibility”—and global norms enshrined in UNSCR 1325 to buttress their participation in peace work.

Challenges Implementing the Women, Peace, and Security Agenda in EU Peacekeeping
Planning staff in EU peacekeeping and crisis management missions maintain traditional understandings of security as a gender-neutral domain in relation to which “gender issues” are seen as an afterthought—not as essential to security work itself