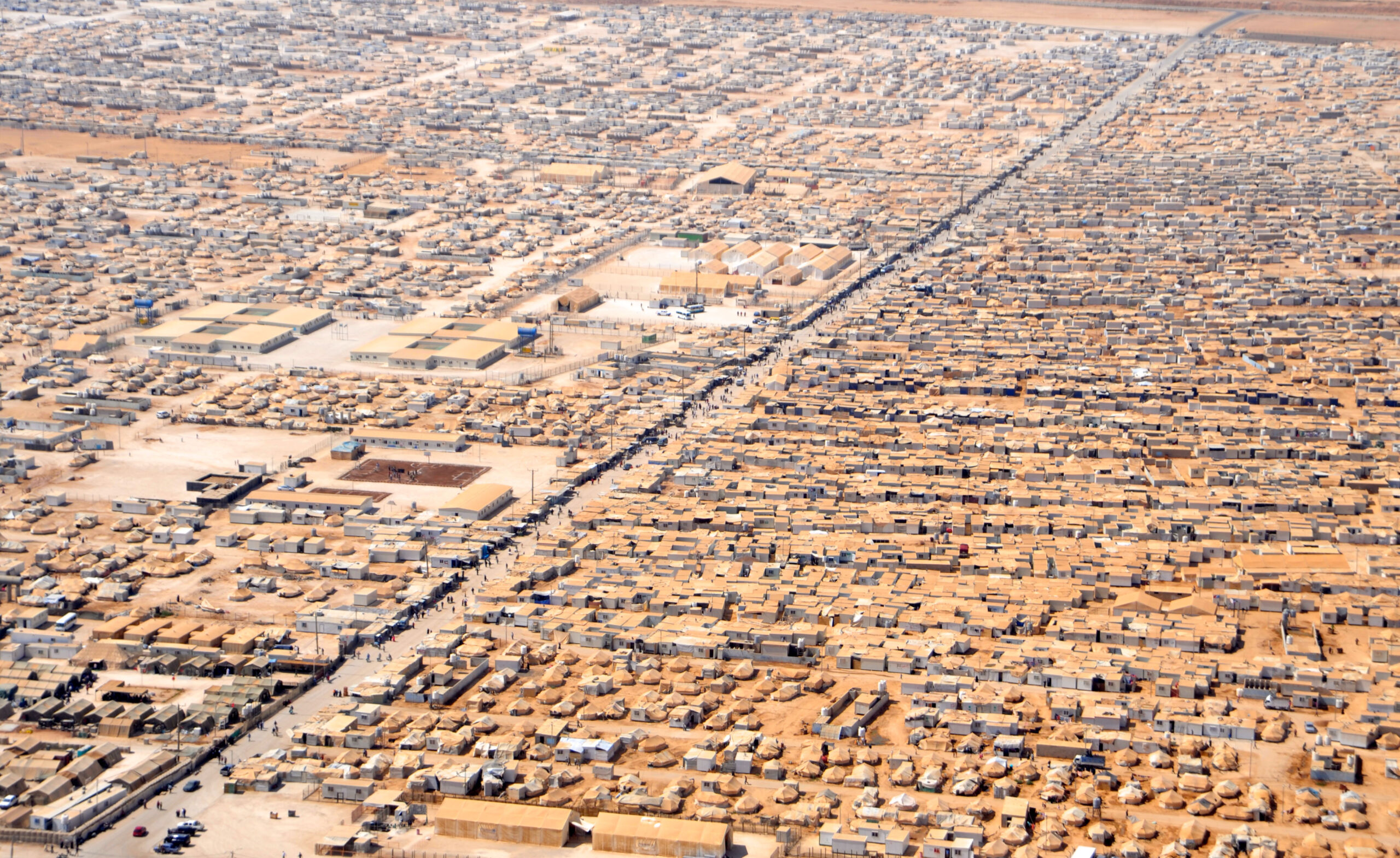

Challenges to Integrating Refugees into the Formal Economy in Jordan
The Jordan Compact is a work program for Syrian refugees created by the Government of Jordan and numerous international partners that frames refugees not just as “objects of humanitarian care” but as “unused human capital, which can be made productive.”
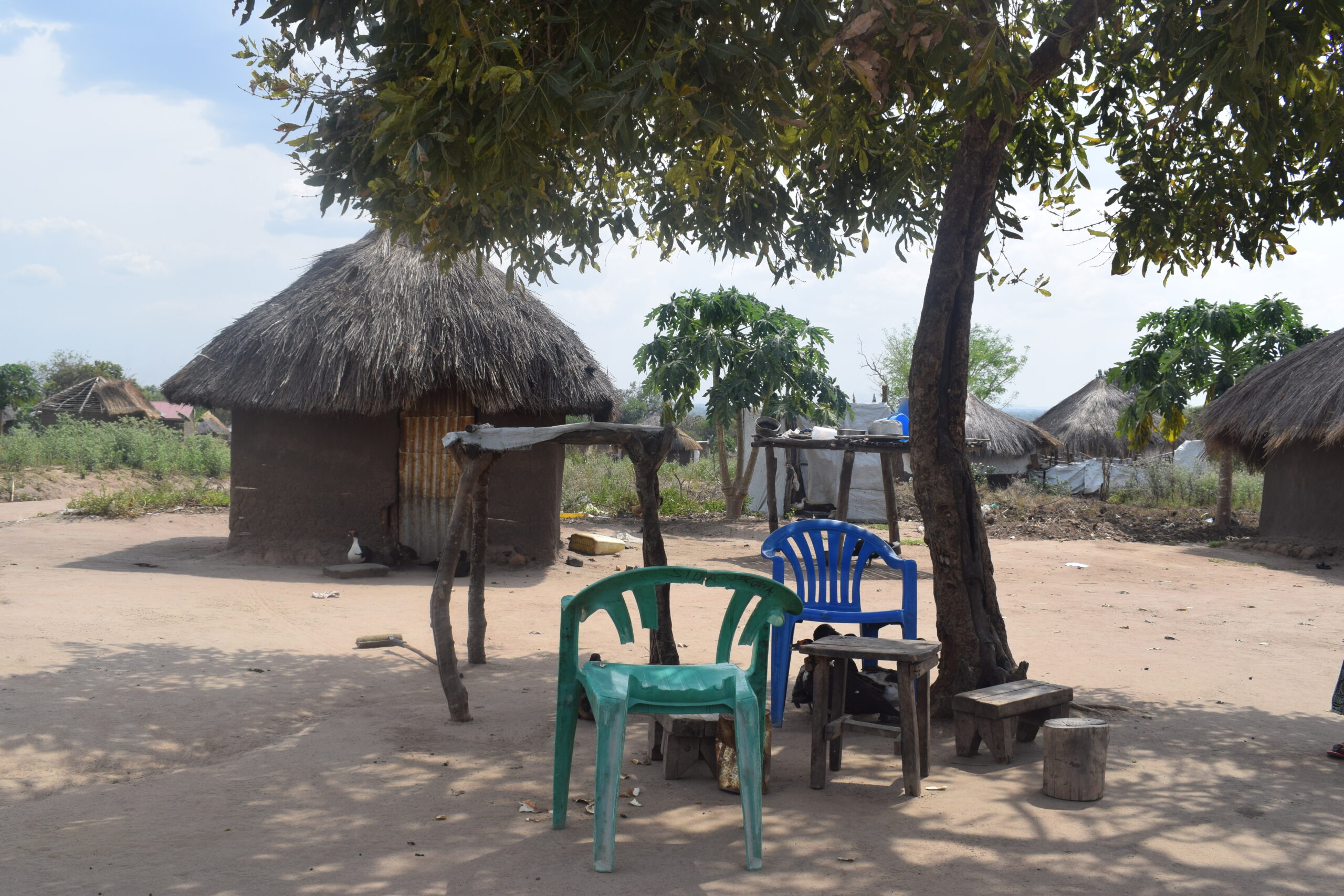

What Makes Some Refugees More Likely to be Approached for Armed Group Recruitment?
Refugees who exhibited a greater degree of relative economic deprivation, who knew someone who had been recruited into an armed group, or who had previous combat experience were more likely than others to be approached for recruitment into armed groups.
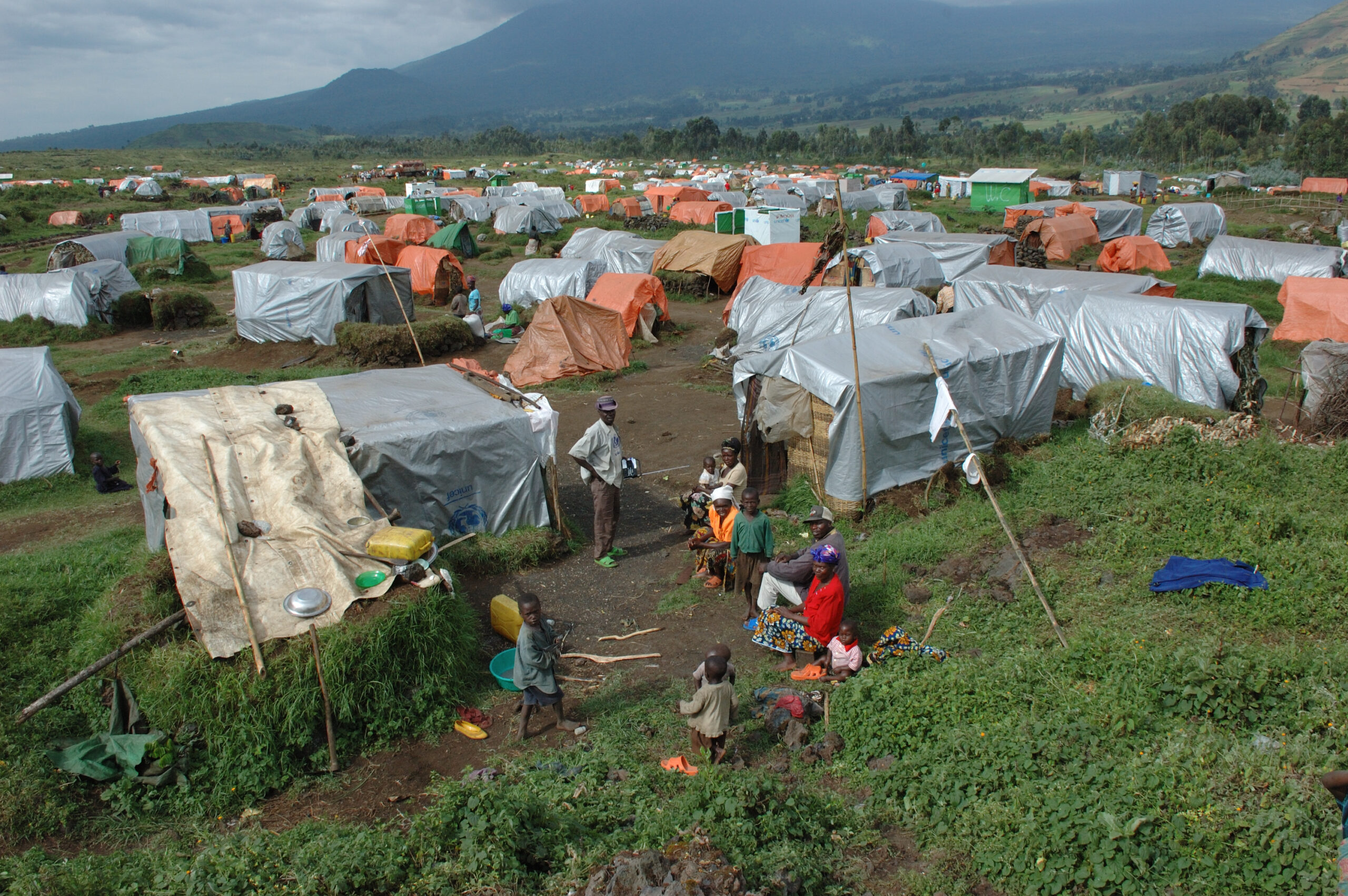

The Refugee Crisis and Seeing the World Through the Eyes of Others
Local people take perspectives on refugees by 1) imagining themselves as the foreign “other” or in the refugee situation or 2) making assumptions about the foreign “other” or the refugee situation.
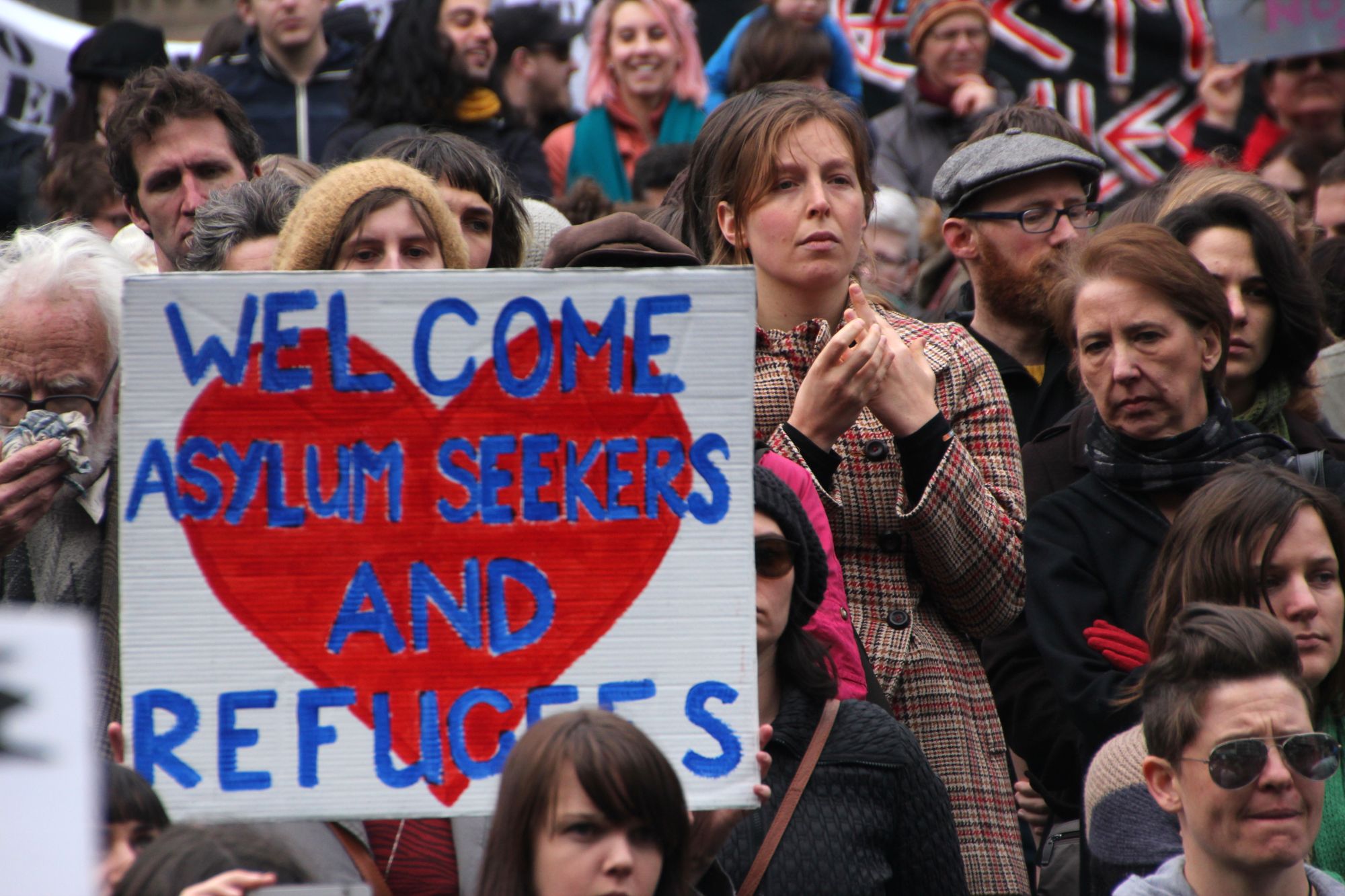
The Importance of Contact Between Refugees and Host Communities
Contact with refugees is associated with a 50% increase in one’s likelihood to strongly support the country’s hosting of refugees and a doubling of one’s likelihood to be willing to hire or to allow one’s children to marry refugees compared to someone who does not have such contact.
Blaming and Targeting Refugees in the Wake of Terrorist Attacks
Prevalent governmental violence against refugees is 47% more likely in the wake of a terrorist attack, and it is probable that this violence is a form of scapegoating against refugee communities rather than a direct means to greater security.
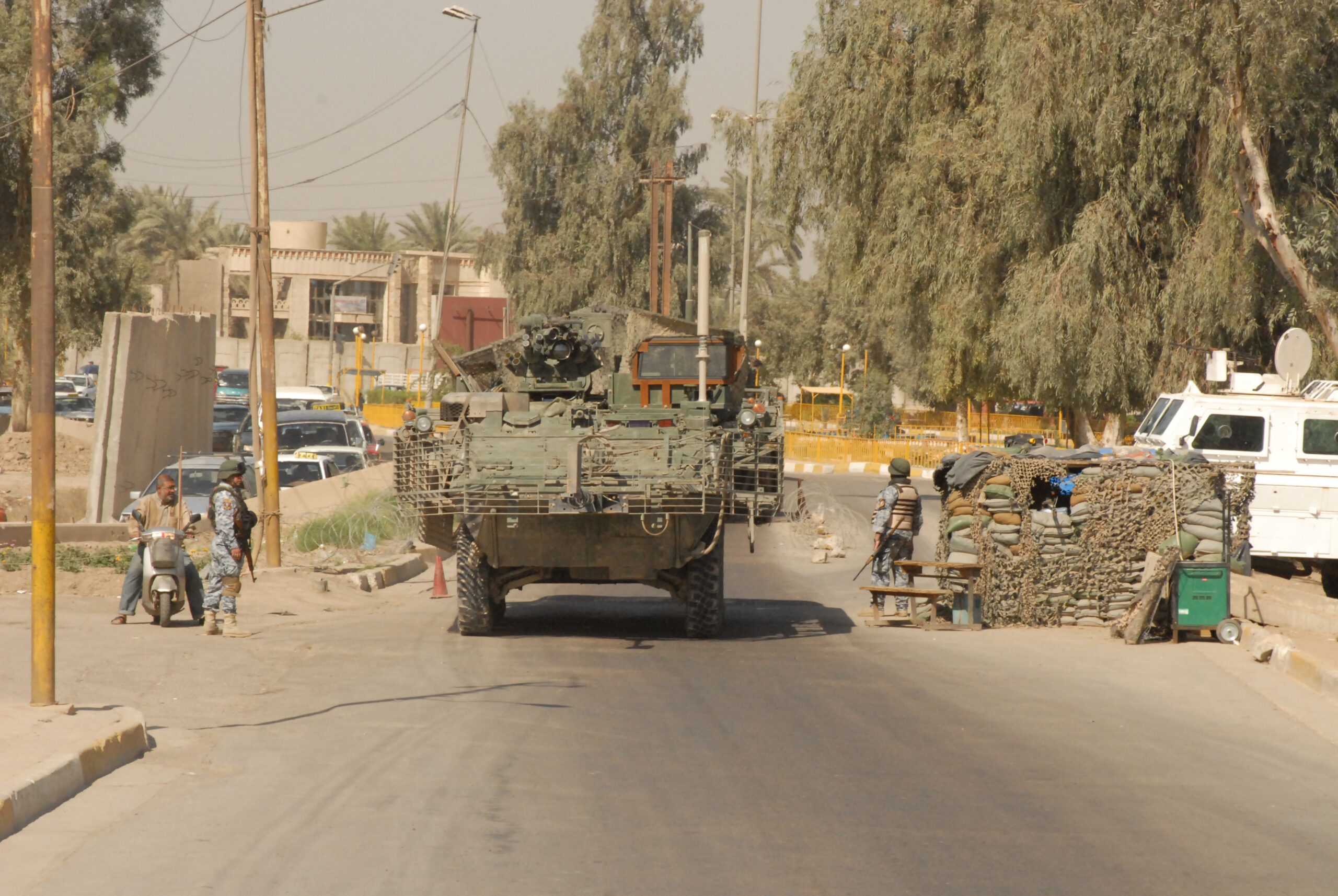

How Feelings Make Military Checkpoints Even More Dangerous for Civilians in Iraq
An average of one Iraqi civilian was killed at a coalition checkpoint each day between 2006 and 2007.

Resisting Exclusionary Nationalism During the Bosnian War
The city of Tuzla was able to resist exclusionary nationalist forces during the Bosnian War due to its identity formation from 1878 to 1990 as a “multi-ethnic working class society with strong anti-fascist, anti-nationalist ideals.”

The Unintended Consequences of UN Peacekeeping’s Use of Security Contractors
The UN’s heavy reliance on security contractors in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) results in more money for institutions and groups that are perceived as corrupt and/or sources of insecurity for many Congolese people.

“Uncivil” Society Organizations in Bougainville and Timor-Leste: Subverting Transitional Justice in Post-Conflict Settings
In Bougainville and Timor-Leste, uncivil society groups were composed of ex-combatants and/or marginalized communities who felt that they were excluded from the peace and reconciliation process.

Traditional Governance and the Maintenance of Peace in Sub-Saharan Africa
Traditional governance, including local chiefs, kings, or conflict resolution mechanisms, can play a powerful role in maintaining peace if it is integrated with the public administration of the state (a scenario called “institutional hybridity”).

Nonviolent Movements for Social Change Considered More Moral and Supportable
Reformists in Iran were more willing to support and join a hypothetical Green Movement in the future if it were to use nonviolent rather than violent strategies.
